CYBER SECURITY DEGREE
It may be a perfect time to pursue a cyber security degree in health information. Health care cyber sec is a growing issue. And hacking and security breaches are on the rise. This leaves patient and health plan member records exposed to risk and theft. In fact, in 2016 alone, cyber criminals stole 78.8 million records in a single attack.
A Cyber Security Degree in Healthcare Information is NOT the Same As Healthcare Informatics
A cyber security degree in healthcare information and a health informatics degree sound the same. They both rely on technology. And work with medical and patient data. But other than are distinct. Health Informatics uses info science to classify and manage electronic health records. The aim is to provide better patient care and outcomes.
One example is when a patient fills a prescription. This script might work against another drug they take. If so, an alert notifies the pharmacist of the conflict. As a result of the high tech alert, the patient stays safe. That same script info is transmitted over a network. Cyber sec aims to keep those networks secure. It also bolsters defenses on operating systems.
When applied to health care, cyber sec protocols makes sure of a few things. That medical data stays private and confidential. And that unauthorized users cannot access or tamper with your data.
Why is Cyber Security Important to the Health Care Industry?
There are a few reasons why cyber sec matters so much in the health care industry. One of them is the high cost of data breaches. As a whole, the health care industry stands to lose about $6 billion for a data breach. And hospital data security hacks can cost a single hospital as much as $7 million. That’s because of fines, lawsuits, and reputation backlash.
But the health care industry lags behind others in defense spending. So another reason is risk. Hospitals and insurers hold troves of valuable data. As a result, the sector is an appealing target for hackers. For health care providers and patients, this is a huge problem. Malware and ransomware threaten a few things. Like the privacy, integrity, and access of protected health info.
In fact, hackers may be able to do more than steal data. They monetize billing and insurance data too. Not to mention put people at risk for identity theft and fraud.
Health Care Cyber Attacks
Hackers are looking for weak areas in systems and health care has them. Here are a few recent health care cyber attacks to know about.
Symantec recently found a serious threat. Called the New Orangeworm, it targets the health care sector in the US, Europe and Asia. In fact, it put harmful malware on X ray and MRI machines. And even tinkered with tech meant to help patients fill out consent forms. A recent survey of security pros served up more troubling news. Over half (51%) said health care is the least prepared of all industries. And, 85% predict more crucial attacks in the future.
An unrelated security report shows cyber attacks in the health care sector surged in 2018. So many, in fact, that it ranked as the top targeted industry in the first three months of the year. These reports also note that health care providers are “ripe targets” for hackers. Another issue relates to a health care policy some businesses adopt. Termed, “BYOD” it means you can bring your own device to work. This adds many users on the network. And boosts chances of a security breach.
The only way to prevent this practice is install a policy against it. Then someone has to manage it and make sure it’s working. Here’s why that presents challenges to the industry:
- 81% of health care services permit employees to connect their own devices networks
- 21% scan BYOD devices before they’re engaged with the network
- 74% of businesses don’t encrypt data on their mobile medical devices
Purdue University Global
- Experience world-class education online: Purdue Global offers 180 programs at associate’s, bachelor’s, master’s and doctoral levels
- Courses taught by highly respected faculty members who are experts in their fields
- Competency-based ExcelTrack™ Programs may allow you to earn your degree faster and for less money
Popular Programs
Human Services, Business Administration & Management, Medical Assisting, Early Childhood Education…
Southern New Hampshire University
- Take advantage of some of the nation’s most affordable tuition rates, while earning a degree from a private, nonprofit, NEASC accredited university
- Qualified students with 2.5 GPA and up may receive up to $20K in grants & scholarships
- Multiple term start dates throughout the year. 24/7 online classroom access.
- Offering over 200 online degree
Popular Programs
Business Administration, Psychology, Information Technology, Human Services…
Health Care Information Security Specialization
Many online schools have cyber sec degree programs. These cover the ins and outs of how to protect systems, networks and info. A cyber security degree in health care information covers these basics. And, adds certain classes in order to help you learn the industry.
You may learn, for instance how to protect the health care industry from data breaches and attacks. And to protect personal data vital to the well being of patients, institutions, and society.
Some programs also serve as study guides for exams. Like the:
- Healthcare Information Security and Privacy Practitioner (HCISPP®)
- Certified in Healthcare Privacy and Security (CHPS
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP®)
Health IT Security Degree Course Curriculum
In every Cyber Sec degree program, you’re going to see the usual Comp Sci classics. Courses like Programming and Cryptography are status quo along with Ethics and Law. But what about the more focused stuff? Here’s a more in depth curriculum for your analysis:
- Learn the CIA – confidentiality, integrity, availability – triad. Then apply this security model to operate a computer network
- Enforce the rules directed by HIPAA. That’s the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996. This means apply them to transmission and storage of electronic medical records.
- Use industry standard tools and techniques. With these skills they prevent, detect, and end threats to computer networks.
Skills Developed Include:
- Interact at ease with internal and third party stake holders.
- Learn legal and regulatory rules and how to handle their challenges
- Analyze ethical and legal issues in health care sec and privacy
- Manage health care cyber sec and privacy
- Apply IT physical and technical safe guards specific to health care
- Enhance compliance, and enforcement processes in health care
A sample year one of this Cyber Sec Degree with Healthcare focus can be:
- Intro to Operating Systems (OS)
- Computer Architecture & OS
- Principles of Info Assurance
- Statistics
- Enterprise Security Management
- Network Sec
- Topics in Health care IT
- Intro to Linux
- Digital Forensics
Core Curriculum:
- Digital ForensicsLearners in this course apply forensics tools and methods. They also study ways to investigate incidents, analyze devices, and reporting.
- Patient Privacy RightsThis type of class explores health care privacy and health care info sec. As such, it may discuss regulatory issues. You may also learn how comply with data security, craft policies and procedures.
- Third Party Risk ManagementIn this course you may learn to identify and examine the risks caused by third parties. And about the policies and documents to ensure they comply. As such, side topics explore laws, regulations, contracts, and agreements.
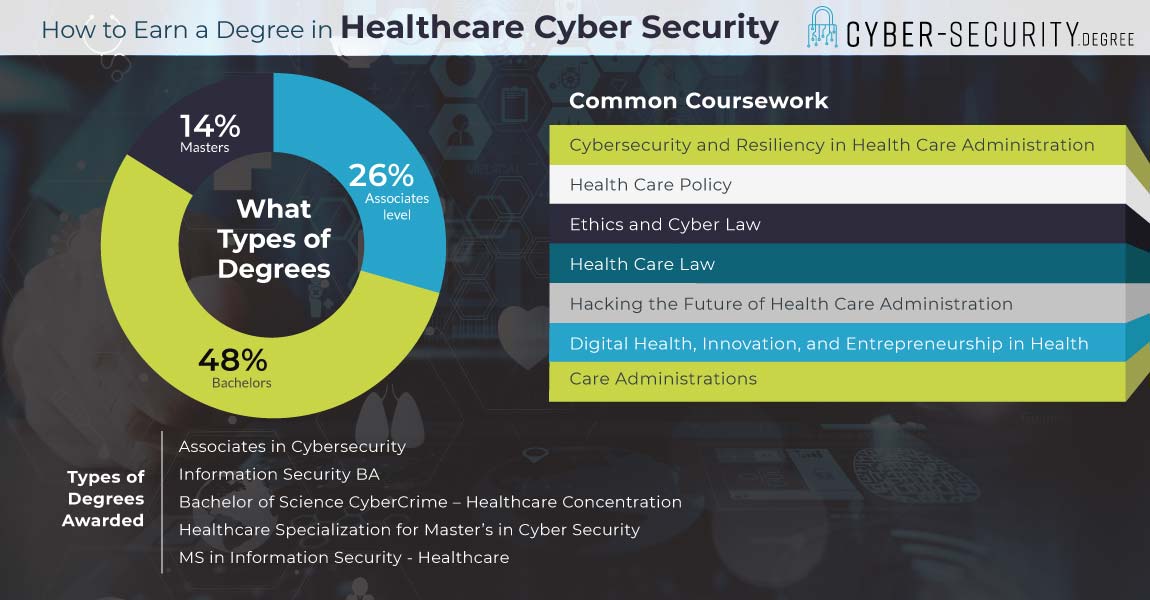
How Long Does It Take to Earn a Cyber Security Degree in Healthcare?
Most working in Info Sec Health care career roles hold a bachelor’s degree at minimum. That means four years of school. This can be started with two years at a community college or Associates program. Then students can complete their bachelor’s at a traditional four year school. Some even go on to complete a two year master’s program after that.
A Cyber Security Degree in Healthcare Information is rare focus for many. But these four year programs are out there. The more common path is to major in some form of Info Sec or Comp Sci. Then a student may either minor in Health care or take specialized classes.
But let’s look at what students learn with a Cyber Sec Healthcare bachelor’s:
- Train in health regulations and standards, including data governance compliance.
- Explore the application of clinical systems like electronic health record systems.
- Learn info system resource management.
- Analyze access, disclosure and storage of protected health info.
Next after a bachelor’s degree is the master’s program. Master’s degrees take about two years to complete. Many who seek a career in Health care Cyber Sec enter an Info Sec master’s program. Then they may focus their courses in the health care relevant courses. Of course, there are also masters programs that focus in Health care Cyber Sec. So, this is what a student may expect to learn at this level:
You’ll prepare for exams like:
- HCISPP®
- CHPS®
- CISSP®
These certs are key for any job of Cyber Sec Health care. That’s because the daily duties on the job involve these very rules of conduct and procedures. Certifications like these are super specific to the jobs at hand. For instance, the HCISPP deals with many detailed compliance matters. It’s these specifics that are on the line when making conduct decisions on the job.
Healthcare Information Systems Security Careers
Information Security Manager
This position is key for maintaining security protocols in a company. They develop strategies to increase network and internet security. Their team management of IT professionals ensures easy access to data. while maintaining high standards for confidentiality and data security. They locate and prevent issues in software or hardware equipment.
Daily duties:
- Create and execute policy and audit plans
- Identify security risks and operation needs
- Review configuration and updates for software and infrastructure protection
- Lead security and policy training
- Assist creating compliant, secure systems
- Manage security testing platforms
- Guide forensic investigations and mitigation procedures
Skills needed to perform all these tasks include Security Risk Management. Also, IT Security & Infrastructure and Cyber Sec is a critical skill. These skills correlate with above average pay.
Information Security Analyst
These analysts plan and carry out security measures. This works in order to protect an company’s computer networks and systems. Their responsibilities expand and evolve as the number of cyber attacks increases. One key part of their work is to create a disaster recovery plan. This is the procedure IT employees follow in case of emergency. These plans allow for the continued operation of an organization’s IT department. The recovery plan includes preventive measures. They copy and transfer data to an offsite location as part of this. It also involves repeat testing the steps in their recovery plans.
Info Sec Analysts do the following:
- Check networks for security breaches and investigate violations
- Install software, firewalls and data encryption programs
- Report on security breaches and the extent of their damage
- Conduct pen testing to simulate attacks
- Assess and fix vulnerabilities found in said testing
- Research the latest IT security trends
- Develop security standards and practices
Information Security Specialist
These Specialists develop and install security measures. They analyze existing security procedures then take measures to increase security. Information security specialists recommend new technologies or policy modifications. They also research and plan to mitigate security risks. This is how they develop systems and techniques. Information security specialists assess security to compare previous and current risk performance. They examine infrastructure and devices. This is how Specialists identify security flaws. Then they can follow up with a prompt solution.
Daily Tasks
- Design audits of computer systems to ensure operational security and protection from attack.
- Oversee information security department.
- Coordinate departments for training on security protocols.
- Maintain policies and standards for information technology-related controls.
Types of skills for this position that increase pay above average:
- Security Policies and Procedures
- IT Security & Infrastructure
- Security Risk Management
- Security Testing
- Auditing
- Cyber Security
| Career | Entry level education | Average Median Salary | Projected growth rate |
Information Security Manager | Master’s degree | $111,385 | 12% |
Information Security Analyst | Bachelor’s degree | $98,350 | 28% |
| Information Security Specialist | Bachelor’s degree | $75,435 | 11% |
Certifications for Cyber Security Degree in Healthcare Information Professionals
CISSP: Certified Information Systems Security Professional
Created by (ISC)2, this cert deals with security policy and management. This may not be the first certification you go after as candidates need at least 5 years of experience before they can take the exam. Your experience must cover at least two of these knowledge areas:
- Security and Risk Management
- Asset Security
- Security Engineering
- Communications and Network Security
- Identity and Access Management
- Security Assessment and Testing
- Security Operations
- Software Development Security
To remain current, cert holders must also join the (ISC)2 and renew every three years. Beyond this, CISSPs have to pay an $85 maintenance fee each year, and, submit 40 continuing professional education (CPE) credits each year.
HCISPP Professional Certification
HCISPP professionals have certified their skills at securing patient health info. The cert holder has foundational knowledge and experience in the privacy and security of health care information. Professionals with HCISPP certification are instrumental in many job functions, such as:
- Risk analyst
- Privacy officer
- Privacy and security consultant
- Practice manager
- Medical records supervisor
- Information technology manager
- Information security manager
- Health information manager
- Compliance officer
- Compliance auditor



