What is a Cryptographer?
A cryptographer is someone who uses codes and ciphers to keep information safe. These pros often work in the cyber security field. So, they protect data and messages that are stored and sent using technology. Cryptographers use knowledge from a few different fields. These include math, computer science, and information security. And, these pros may work in different industries. Banking, government, the military, and communications are just a few areas where sensitive info needs to be protected. So, employers in these areas may hire workers who know cryptography.
WHAT IS A CRYPTOGRAPHER RESPONSIBLE FOR?
Cryptographers are typically in charge of protecting data like passwords, messages, or financial info. This is important for both businesses and consumers. Think about buying something online. When you input your credit card number on a website, you likely trust that it won’t fall into the wrong hands. That’s because cryptographers are behind the scenes, making sure your personal info stays safe.
These pros may use different methods to protect data. One key method is encryption. This is the process of turning information into code. So, only the intended recipient can see the data or read the message. Cryptographers may also use algorithms, ciphers, and other security measures.
Another important job duty is keeping up with the times. Cyber security changes fast. Hackers often come up with new ways to get around security measures. So, those who work in this field need to stay on top of new threats. All these duties add up to an important goal: keeping hackers and criminals from getting sensitive info. This keeps businesses and their customers safe. And, it prevents government and military secrets from being leaked.
What Are Various Career Paths to Becoming a Cryptographer?
You may get some idea of how to become a cryptographer by looking at similar IT security roles – like Information Security Analyst. Here are three possible paths:
- Go from college to a pursue cryptography career path. Often times, employers look for work experience. That said, an Information Security Analyst generally needs a minimum of a Bachelor’s degree. This should be in a field like computer science, information assurance, or programming.
- Earn a Master’s to pursue a cryptographer career. Some employers prefer to hire workers with a Master’s degree. For Security Analysts, that often means a Master of Business Administration (MBA) in information systems. Expect to take courses in computer subjects, along with business.
- Education + related work experience. You will likely need to earn at least Bachelor’s degree in computer science or a related major. Besides that, work experience could help you pursue your dream job. Many information security experts get their start in an entry level job. They may work in a related IT role before going deeper into the cyber security field. For instance, experience in a database admin job could help you pursue a database security role.
What Degrees do Employers Prefer a Cryptographer to Have?
Most computer and information technology jobs need at least a Bachelor’s degree. To get an idea of what kind of education a cryptographer needs, you could look at related roles. Like, Information Security Analyst. Earning a Bachelor’s degree could be enough to pursue a cryptography career path. For Information Security Analysts, this is the minimum amount of education needed. The degree should be in computer science or a related area. You may build general knowledge of computers and networks, and how to protect them.
You are not likely to find a Bachelor’s program in cryptography, itself. But, you could find a related program. Like, a Bachelor of Cyber Security program. This may cover the basics of keeping info safe and stopping cyber attacks.
Some employers look for workers who have earned a Master’s degree. It’s rare to find a Master’s program in cryptography. But, you could find related programs. Think, a Master’s in Cyber Security, or an MBA in Information Systems. Programs like this may teach cryptography along with many other subjects. In short, if you’re interested in a cryptographer career, you’ll likely need to pursue education that covers more than just cryptography.
Southern New Hampshire University
- Take advantage of some of the nation’s most affordable tuition rates, while earning a degree from a private, nonprofit, NEASC accredited university
- Qualified students with 2.5 GPA and up may receive up to $20K in grants & scholarships
- Multiple term start dates throughout the year. 24/7 online classroom access.
- Offering over 200 online degree
Popular Programs
Business Administration, Psychology, Information Technology, Human Services…
Purdue University Global
- Experience world-class education online: Purdue Global offers 180 programs at associate’s, bachelor’s, master’s and doctoral levels
- Courses taught by highly respected faculty members who are experts in their fields
- Competency-based ExcelTrack™ Programs may allow you to earn your degree faster and for less money
Popular Programs
Human Services, Business Administration & Management, Medical Assisting, Early Childhood Education…
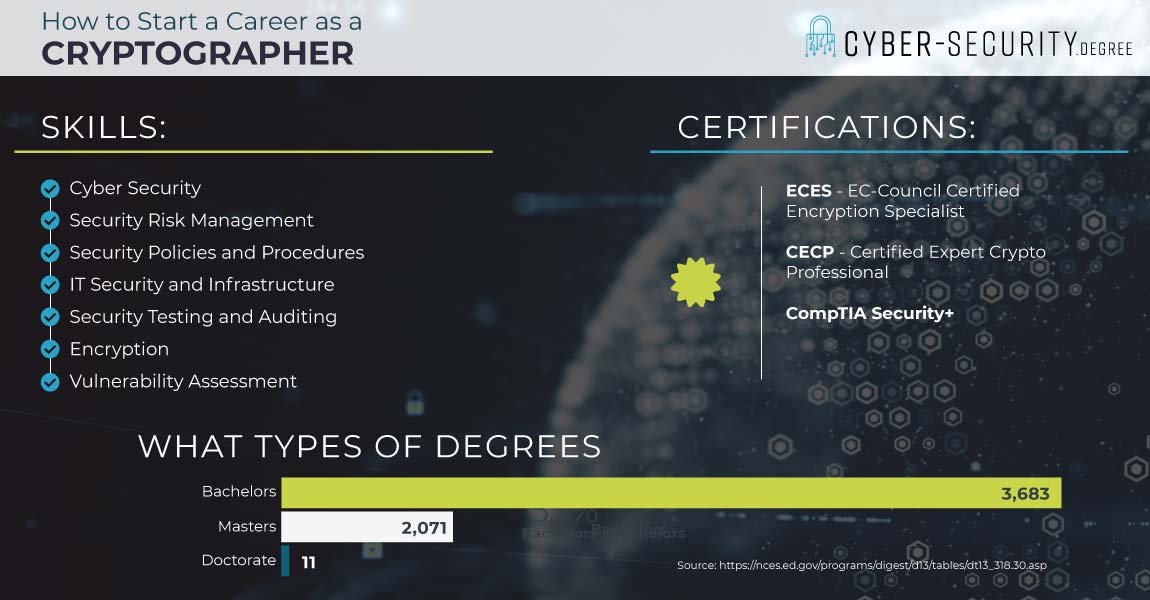
WHAT SKILLS DO YOU NEED TO BE A CRYPTOGRAPHER?
Cryptographers may have skills ranging from encryption to decoding. That said, many workers in the cyber security field have broader skill sets. So, they may know cryptography. But they could also have other key skills that businesses look for. These include:
Cyber Security – This is the practice of defending computers, networks, and more from threats. It involves stopping attacks, plus preventing future attacks. You could study cyber security in a college degree program. And, you may also be able to enhance this skill on the job.
Security Risk Management – This skill is all about finding IT security risks. These are weak spots that that others could exploit. Experts need to know where the weak spots are, and why they are a problem. Then they make a plan to reduce risk. You could learn this skill in a college program and enhance it on the job. The Security+ certification also covers risk management.
Security Policies and Procedures – Cryptographers need to know the rules and practices for using IT safely at their workplaces. (IT pros like Information Security Analysts help plan these policies.) You could study the theory behind IT security procedures, in college. And, you could learn your company’s IT policies on the job.
Cryptographer Salary
You might be able to get an idea of a cryptographer’s salary by taking a look at what Cyber Security Engineers earn. The median earnings for these pros is $96,000. The bottom 10% of earners may make $65,000. And, the top 90% could earn $137,000.
Cyber Security Engineers may earn more as they gain experience. An entry level role in this field may pay about $75,000. At mid career, the role could pay about $101,000. Right now, about 5.9% of workers in this career path are in entry level roles. 29.6% are early in their career. 27.4% are at mid career. And, 37% are experienced.
Top Paying Cities
Workers in the cyber security field could earn more if they learn certain skills. For instance, Cyber Security Engineers who know security risk management may earn 12% more. Those who know security testing and auditing may also earn 12% more.
| City | Median Salary | % of People with 1-4 Years Experience |
| New York, NY | $109,000 | 42.4% |
| San Diego, CA | $106,000 | 29.6% |
| Arlington, VA | $98,000 | 59.4% |
CRYPTOGRAPHER Certifications
- EC-Council Certified Encryption Specialist (ECES). This cert covers crypto basics. In the prep course, you’ll learn modern symmetric and key cryptography. That includes algorithms like Feistel Networks, DES, and AES. And, you’ll learn other security concepts, like how to set up a VPN. Earning the cert may be perfect for IT security pros who want to better understand cryptography. Like, penetration testers and ethical hackers. In other words, it could be a great way to learn new skills and enhance your career.
- Certified Expert Crypto Professional (CECP) Earning this cert proves your knowledge of key cryptography concepts and security needs. You’ll need to know about ports, interfaces, and a lot more. And, you’ll need to be familiar with the Finite State Model. This cert is considered intermediate. So, you’ll need three years of work experience. Preparing for CECP could help you learn new skills and pursue the next step in your career.
- Security+< This course covers key skills needed for IT security roles. That includes areas like managing risk and spotting an intrusion. Of course, cryptography is one of the areas covered. You could learn how to install and configure wireless security settings. And, you could learn how to put public key infrastructure in place. This cert may be great if you hope to enhance your cyber security career.



